oxidase test for pseudomonas aeruginosa|Oxidative : Bacolod Spot Indole Test Method. Place several drops of 1% p . The Official site of the city of Las Piñas. Search; Menu; Our Home. Showcase of dynamic modern communities, historical sites, and effective local governance. . The Best legacy of the city government to the youths of Las Piñas. Read More. Clean and Green Environment. Las Piñas is one of the highly urbanized cities in the Philippines with .
PH0 · Pseudomonas aeruginosa
PH1 · Oxidative
PH2 · Oxidase Test: Principle, Procedure, Results • Microbe
PH3 · Oxidase Test Protocol
PH4 · Oxidase Test
PH5 · Fast and specific detection of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from
PH6 · Biochemical Test and Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
PH7 · 12.6.4: Oxidase Test
PH8 · 1.24: Oxidase Test
1.1 These Promotion Specific Terms (the “Promotion Specific Terms”) contain the specific terms and conditions which govern the “Casino Offer – Bet $20 on any Casino Style Game at OLG.ca, Get a $200 Casino Bonus” (the “Promotion”).
oxidase test for pseudomonas aeruginosa*******Ago 10, 2022 Spot Indole Test Method. Place several drops of 1% p .This test is used to assist in the identification of Pseudomonas, .
The oxidase test is a biochemical reaction that assays for the presence of cytochrome oxidase, an enzyme sometimes called indophenol oxidase (2, 10, 12). In the presence . The oxidase test is a technique for detecting the presence of the terminal enzyme system in aerobic respiration called cytochrome C oxidase or cytochrome a3. .
The oxidase test is a biochemical testing module used to assay the ability of bacteria to synthesize cytochrome c oxidase enzymes. This test was first introduced by Gordon and McLeod in 1928 to .oxidase test for pseudomonas aeruginosa Biochemical test kits such as API 20 NE are commonly used for identification; 4 however, a high rate of misidentification of oxidase positive Gram .
The oxidative-fermentative test is used to determine if gram-negative bacteria metabolize carbohydrates oxidatively, by fermentation, or are nonsacchrolytic and therefore have no .
For example, the gram-negative opportunist Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the gram-negative cholera-causing Vibrio cholerae uses cytochrome c oxidase, . Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore forming rod that is capable of causing a variety of infections in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts. [1] .Pseudomonas aeruginosa and most other glucose non-fermenting, Gram-negative bacilli are oxidase-positive. Except for the genus Plesiomonas, the glucose fermenting .
oxidase test for pseudomonas aeruginosa OxidativePseudomonas aeruginosa and most other glucose non-fermenting, Gram-negative bacilli are oxidase-positive. Except for the genus Plesiomonas, the glucose fermenting .The P. aeruginosa aerobic terminal oxidases include enzymes that can use ubiquinol or cytochromes as electron donors, ones that have low or high affinities for O 2, and a cyanide-insensitive oxidase (CIO) that functions in the presence of this endogenously produced virulence factor ().Aside from CIO, the four other aerobic terminal oxidases encoded by .Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram-negative rod.Pseudomonas aeruginosa can resist high concentrations of salt, dyes, weak antiseptics, and many commonly used antibiotics. Most pseudomonads known to cause disease in humans are associated with opportunistic infections. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas maltophila are mostly .
The oxidase test is used to determine whether an organism possesses the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. . Practical laboratory test for the identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of bacteriology. 74, 356–358. Gilani M, Munir T, Latif M, Gilani M, Rehman S, Ansari M, Hafeez A, Najeeb S, Saad N. 2015. In Vitro Efficacy of Doripenem .

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, . which will test positive for oxidase. Confirmatory tests include production of the blue-green pigment pyocyanin on cetrimide agar and growth at 42 °C.
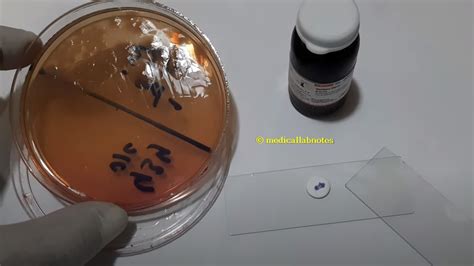
Pseudomonas species are ubiquitous in soil and although some have long been recognized as plant pathogens , . Gram stain, oxidase test, interpretation of differential media, and the use of micropipettors and microcentrifuges. These exercises are scheduled as the final project of the semester to give students the opportunity to apply .In the oxidase test, artificial electron donors and acceptors are provided. When the electron donor is oxidized by cytochrome oxidase it turns a dark purple. This is considered a positive result. In the picture below the organism on the right (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) is oxidase positive.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common, free-living, Gram-negative bacterium that can cause significant disease as an opportunistic pathogen. Rapid growth, facile genetics, and a large suite of virulence-related phenotypes make P. aeruginosa a common model organism to study Gram-negative opportunistic pathogens and basic microbiology. This unit . There are two ways to do the oxidase test, one is using a filter paper (see image 2 below) and the oxidase reagent and the second is doing a ‘plate’ oxidase test (image 3). Image 2: Oxidase test on filter paper. A positive oxidase result given by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (left) is indicated by a purple color. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is a condition that can affect your skin, blood, lungs, GI tract and other parts of your body. Pseudomonas bacteria are common in the environment, especially water, soil and produce. Symptoms vary according to where the infection is in your body. Treatment usually includes at least one type of .
Pseudomonas fluorescens not only enhances the plant growth but also. controls the fungal pathogens by p roduction of anti fungal metabolites. The. objective of this exper iment was to identify P .FIG. 2. Oxidative -fermentative test inoculated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acid production in the open tube and not the oil -covered tube indicates an oxidative result. (a) P. aeruginosa incubated for 24 hours. Note pH change in the top of the open tube only. (b) P. aeruginosa incubated for 48 hours. Note the diffusion of the acid down Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative environmental and human opportunistic pathogen highly adapted to many different environmental conditions. It can cause a wide range of serious infections, including wounds, lungs, the urinary tract, and systemic infections. The high versatility and pathogenicity of this bacterium is attributed .The oxidase test is based on the bacterial production of an oxidase enzyme. Cytochrome oxidase, in the presence of oxygen, oxidizes the N-N-N-tetra-methyl-p-phenylenediamine oxidase test reagent in a Gibson oxidase swab. . Pseudomonas aeruginosa and most other glucose non-fermenting, Gram-negative bacilli are oxidase-positive. Except for the .Abstract. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a prevalent, opportunistic, Gram-negative bacterium that infects immunocompromised individuals, frequently causing hospital-acquired and community-acquired infections. Currently, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most widespread and fatal agents among the various causes of nosocomial .Oxidative Introduction. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative pathogen that is commonly associated with hospital-acquired infections, infections in immunocompromised hosts, and chronic infections in patients with structural lung disease such as cystic fibrosis (CF). For this review, we sought to update the readers with regard to the epidemiology .Infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Biochemically, P. aeruginosa can be confidently identified on the basis of (1) a positive oxidase test, (2) a triple sugar iron agar reaction of alkaline over no change, and (3) growth at 42oC. Other key biochemical characteristics include oxidation of glucose but not disaccharide, hydrolysis of .
The oxidase test is a biochemical test used to determine the presence of the oxidase enzyme in bacterial cells. The test involves adding a reagent containing an artificial electron acceptor to a bacterial sample and observing the color change that occurs. The test is used to identify certain groups of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Neisseria . Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative bacillus considered an opportunistic pathogen, usually associated with nosocomial infections in immunocompromised patients. Among the infections caused .
Detailed seat map Etihad Airways Boeing B777 200LR. Find the best airplanes seats, information on legroom, recline and in-flight entertainment using our detailed online seating charts. . Boeing B777 300ER 2 class V1; Boeing B777 300ER 2 class V2; Boeing B777 300ER 3 class; Boeing B787 10; Boeing B787 9 three class; .
oxidase test for pseudomonas aeruginosa|Oxidative